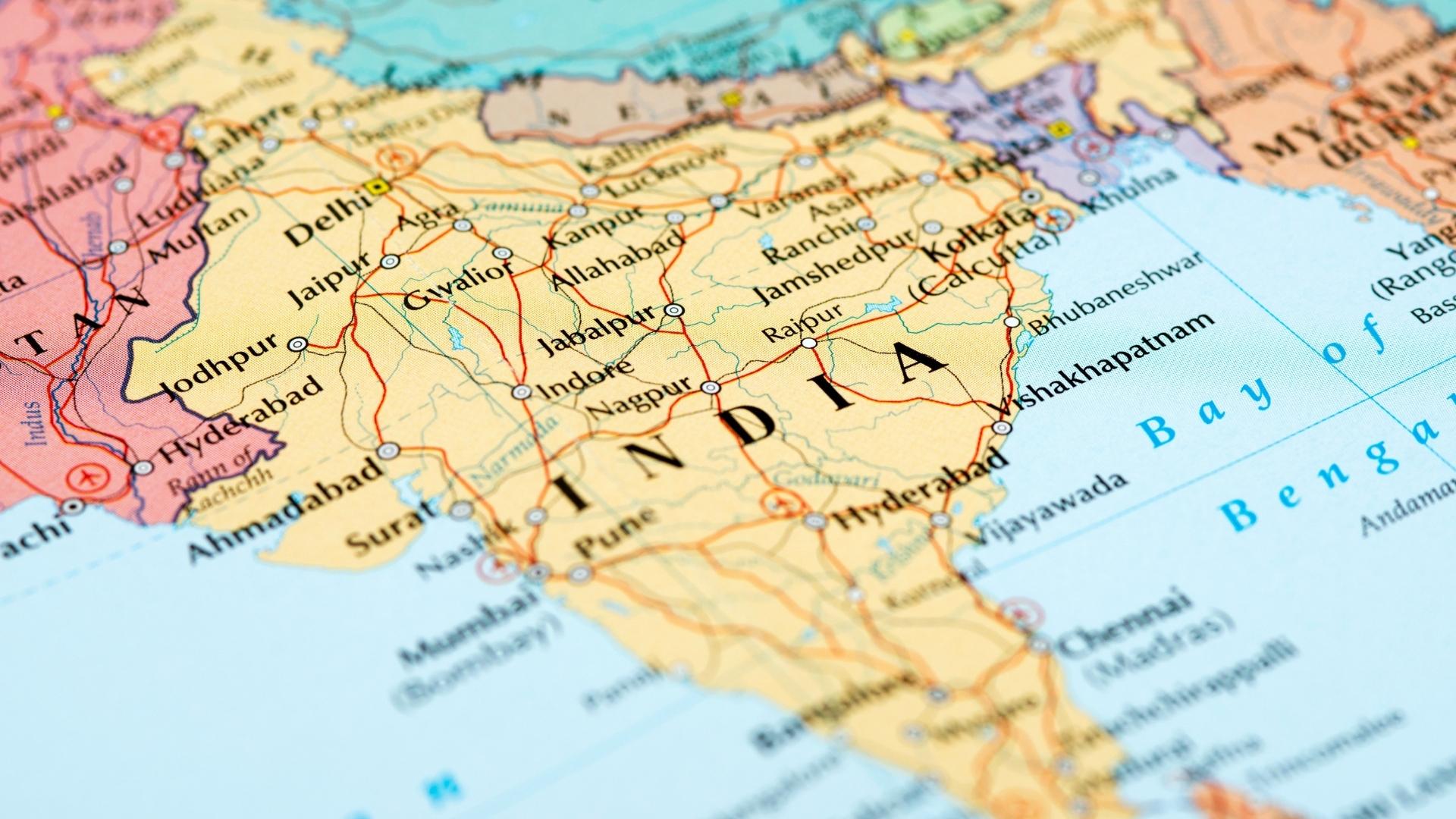
India, one glorious land standing for ages, witnessing the diverse change in its geographic boundaries and extremities of various ethnicities, customs, traditions and cultures. Being the 7th largest country in the world with a rich cultural heritage, India has been home to several major religions of the world such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, Islam, Christianity and others, this prosperous land endured numerous foreign invasions in the past. Unique geographical features separate India from the rest of Asia, an iconic nation stretches from Great Himalayas in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
General Information
National Flag
Based on the flag of Indian National Congress which was designed by Pingali Venkayya of Andhra Pradesh, the present National Flag was adopted by the Indian Constituent Assembly on July 22, 1947. It is well known as “Tri-Colour Flag”, the top panel is of saffron colour representing courage and sacrifice, the middle panel is of white colour with Ashoka chakra representing truth, peace and purity, and the bottom panel is of green colour representing prosperity.
National Emblem
Sarnath Lion Capital of Ashoka, is the national emblem of India. It was adopted on January 26, 1950. The emblem comprises of four lions facing in four directions mounted back to back, empanelled on a circular abacus that has sculptures in alto-relievo of an elephant, a lion, a bull and a galloping horse separated by arbitrating dharma chakras. The words “Satyameva Jayate” are inscribed on the emblem, were taken from Manduka Upanishad, and it means “Truth Alone Triumphs”.
National Anthem
The song titled “Jana Gana Mana”, originally composed in Bengali by Rabindranath Tagore. It was first sung on December 27, 1911 at the Calcutta Session of Indian National Congress. The song was translated into English by Rabindranath Tagore in 1919, under the title ‘Morning Song of India’. Its Hindi Version was adopted on January 24, 1950.
National Song
The national song is ‘Vande Mataram’, originally composed by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee in Sanskrit. It was first sung in 1896, at the Calcutta Session of Indian National Congress. It was translated in English by Sri Aurobindo. The time to be taken to sing it is one minute and five seconds. It is in Taal Kaherwa.
National Animal
The national animal is Royal Bengal Tiger (Panthera Tigris). It is found throughout the mainland. Till 1972, Lion was considered as a National Animal.
National Bird
The most colourful and with grace, the Indian peacock is considered as the national bird of India.
National Tree
Banyan tree is considered as the national tree of India.
National Flower
Lotus is considered as the national flower of India.
National River
The national river is Ganga, it is the longest river of India. It originates from the Gangotri Glacier of the Himalayas.
National Game
Hockey has been considered as the national game of India since time immemorial. However, in 2012, the clarification by the sports ministry stated that it has not declared any sport as national game of India. Thus, India does not have an official national game.
National Calendar
The national calendar of India is the Saka Calendar, which was introduced by Calendar Reform Commitee in 1957, and its usage officially started at 1 Chaitra 1879 Saka Era (March 22, 1957). However, India follows Gregorian Calendar along with the Saka Calendar for certain official purposes.
Indian Currency
The Indian Currency is Rupees. The Reserve Bank of India has the sole authority to issue currency notes. The coins are minted by four government mints at Mumbai (Maharashtra), Alipore (West Bengal), Cherlapally (Telangana) and Noida (Uttar Pradesh).
Geographical Information
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Geographic Co-ordinates | Reclining in the northern hemisphere, the mainland extends between 8° 4′ and 37° 6′ north latitudes, and 68° 7′ and 97° 25′ east longitudes. |
| Indian Standard Time | GMT (Greenwich Meridian Time) + 05:30 |
| Area | 3,287,263 square kilometres |
| International Borders | India shares its borders with Pakistan to the west, Afghanistan to the north-west, Nepal, Bhutan and China to the north, Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. Longest border is with Bangladesh and the shortest is with Afghanistan. |
| Borderline | 15200 kilometres |
| Coastline | 7516 kilometres (including the Mainland, Lakshadweep islands and Andaman & Nicobar islands) |
| Physical Features | The mainland includes four regions: The Himalayan Range, Indo-Gangetic Plains, The Desert Region & Southern Peninsula |
| Climate | Seasons classified as: Winter (December to April), Summer (April to June), Monsoon (June to September) and Post-Monsoon (October to December) |
| Natural Disasters | Flash floods, monsoon floods, earthquakes, droughts and landslides |
| Environmental Issues | Air pollution, deforestation, energy conservation, solid waste management, oil and gas conservation |
Demographic Information
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Population | India is the second most populous country in the world with a total population of 1210 million as of Census 2011 (623 million males and 587 million females). 1406.6 million as of 2022. |
| Annual Growth Rate | 1.64% during 2001-2011. 0.9% during 2020-2025 |
| Birth Rate | 20.1 during 2011-2015 |
| Death Rate | 7.2 during 2011-2015 |
| Life Expectancy Rate | 66 years for males; 68 years for females during 2006-2011. 69 years for males and 72 years for females as of 2022. |
| Sex Ratio | According to the Census 2011, the sex ratio is 940 per 1000 males. |
| Literacy | As per the Census 2011, the overall literacy rate is 74.04%, where the male literacy is 82.14% and the female literacy is 65.46%. |
| Languages | Hindi and English are the official languages declared by the Indian Constitution under Article 343. However, there are 22 regional languages have also been officially recognized under Schedule VIII of the Indian Constitution. |
Indian Government
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Name of Country | Republic of India |
| Type of Government | Sovereign, Socialist, Democratic, Republic with a Parliamentarian Government. |
| Capital | New Delhi |
| States & Territories | 28 States & 8 Union Territories |
| Independence | August 15, 1947 |
| Constitution | The Constitution of India came into force on January 26, 1950. |
| Legal System | Prime source of national legal system is The Constitution of India. |
| Executive System | The President of India is the Head of the State. The Prime Minister with the support of Council of Ministers head the Government. |
| Legislature | The Indian Legislature comprises of the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) forming both the houses of the Parliament. |
| Judiciary | The Supreme Court of India is the apex court of the Indian Judiciary, followed by High Courts and other Subordinate Courts. |
Source:
Manorama Year Book 2021, Concise General Knowledge Manual 2021, UNFPA